Duplicate Record Merging in CRM
The Complete, Governed & AI-Ready Guide to Consolidating Duplicate CRM Data
Table of Contents
Duplicate Records in CRM
Duplicate records are unavoidable in Dynamics 365 CRM, whether they originate from data imports, integrations, Power Automate flows, marketing syncs, manual entry, or migrations.
What separates a basic CRM from an enterprise-ready CRM is how accurately, safely, and consistently duplicate records are merged.
What is Duplicate Record Merging in Dynamics 365 CRM?
Duplicate record merging is the process of consolidating two or more duplicate CRM records into one authoritative master record, while:
- Preserving related activities, notes, and relationships
- Applying business rules to determine the correct master
- Merging field and address data intelligently
- Retaining conflicting values for audit and review
- Executing merges manually or automatically
The objective is simple:
One customer. One history. One trusted record.
Why Native Dynamics 365 CRM Merging is Not Enough
Out-of-the-box Dynamics 365 merging is manual and limited, making it risky in real-world CRM environments.
Native CRM Merge Limitations
- Users must manually choose the master record
- No conditional logic to allow, review, or deny merges
- Field values can overwrite correct data
- Address data is treated like regular fields
- No automation during imports or integrations
- No audit transparency for compliance or AI
This makes native merging unsuitable for high-volume, compliance-driven, or AI-enabled CRM systems.
The Complete Duplicate Merge Guide for Dynamics 365 CRM
Enterprise duplicate merging in Dynamics 365 CRM works through four tightly integrated layers, each answering a critical question.
How to decide the Master Record to Merge Duplicates in CRM?
When merging duplicate records in CRM, selecting the right master record ensures data accuracy and prevents information loss.
The master record is typically chosen based on data completeness, recent activity, and overall reliability.
Which record should stay in your CRM after merge?
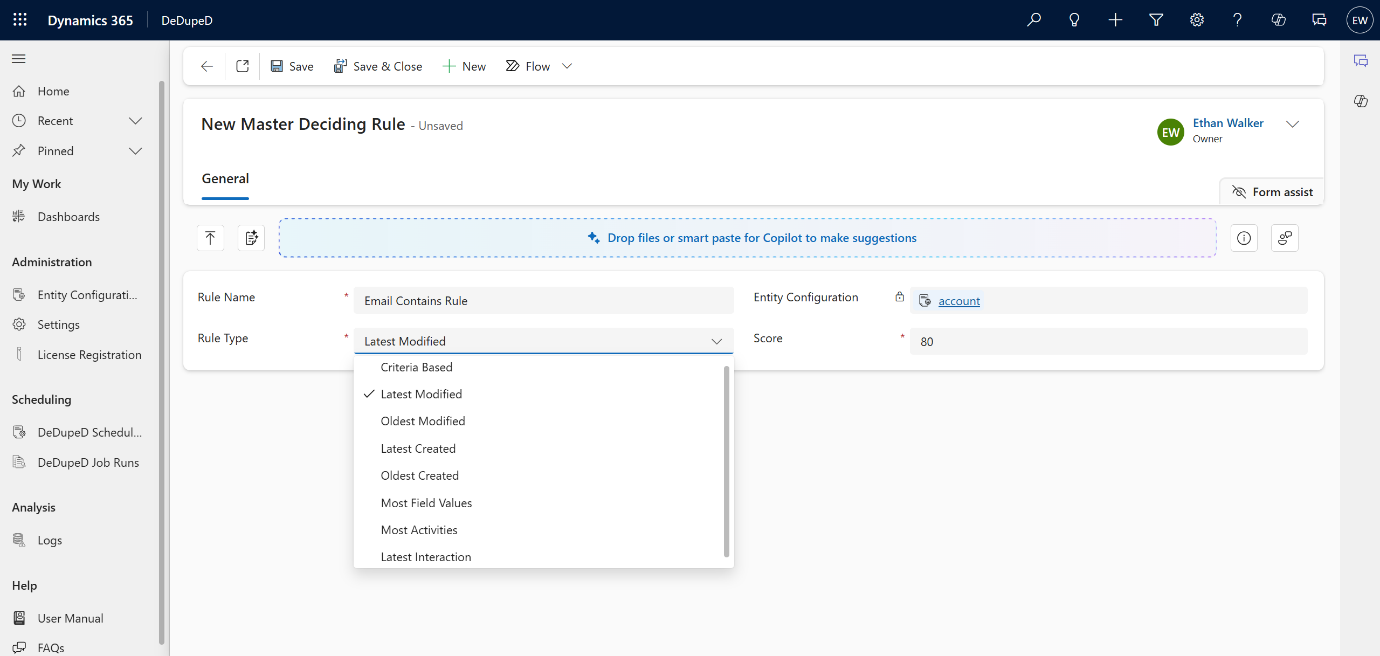
Master Deciding Rules determine which duplicate record survives and becomes the master. For this, you can use any of the master deciding rules as per your business needs. Built-In Master Rule Types:
- Latest Modified
- Oldest Modified
- Latest Created
- Oldest Created
- Most Field Values
- Most Activities
These rules automatically evaluate data completeness, stability, and engagement.
Criteria-Based Master Selection to Merge Records in Dynamics 365 CRM
How to select the master record based on business criteria to merge the records in Dynamics 365 CRM?
Criteria-based master selection uses business-defined conditions to decide which records should remain after a CRM merge.
This ensures duplicate merges follow organizational priorities and maintain data consistency across teams.
For advanced scenarios, master selection can be driven by custom business conditions, such as:
- Always retain Active records
- Prefer records owned by a specific team
- Keep records from a trusted data source
This allows CRM administrators to align merge outcomes with organizational policy.
Scoring-Based Master Deciding Rules for Merging Records in Dynamics 365 CRM
How to select the master record based on the completeness score for merging in Dynamics 365 CRM?
Scoring-based master selection determines the master record by evaluating multiple merge rules together instead of relying on a single condition.
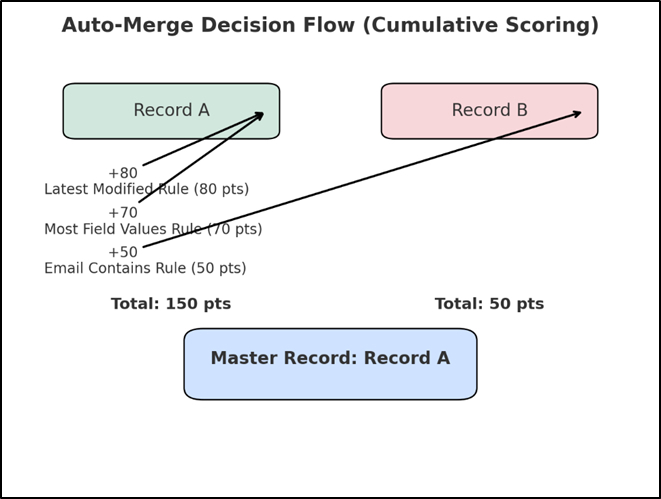
Each record earns a score based on predefined priorities, and the record with the highest combined score is retained, making merge decisions transparent, predictable, and easy to explain.
Multiple master rules can be enabled simultaneously, each with a weight (1–100).
How scoring works:
- All active master rules are evaluated
- Scores are accumulated per record
- The record with the highest total score becomes the master
Example:
- Latest Modified → 80
- Most Field Values → 70
- Email Match → 50
This creates predictable, explainable, AI-friendly master selection.
Looking to standardize how master records are chosen during duplicate merges in Dynamics 365?
Explore how master deciding rules help organizations merge duplicates confidently while protecting critical data.
Smarter Merges with Master Record Suggestions
Smarter merge suggestions assist users by recommending the best master record based on data quality and relevance. This approach combines automation with human judgment, reducing errors without forcing decisions.
During manual merges:
- The system highlights the recommended master record
- Users may accept or override the suggestion
This balances automation with user confidence.
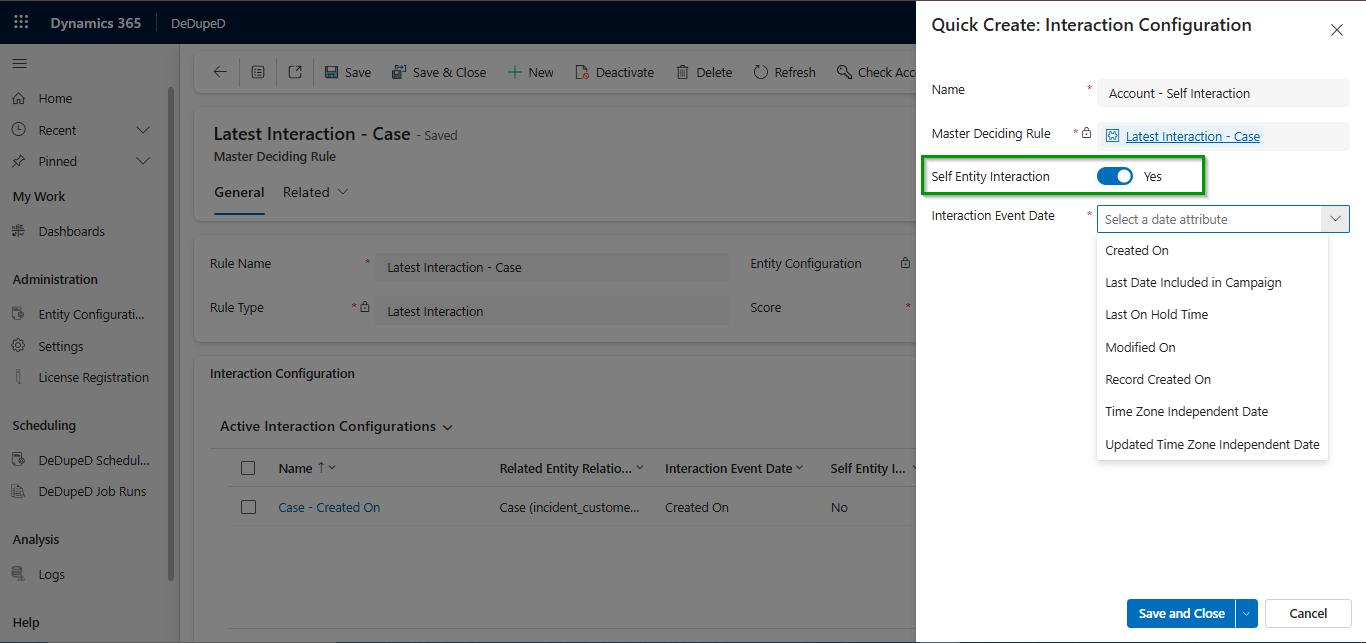
Interaction-Based Master Selection for Merging Records in Dynamics 365 CRM
How to select the master record based on usage to merge the records in Dynamics 365 CRM?
Interaction-based master selection determines the master record during a CRM merge based on recent activity and usage, not just static data. By evaluating interactions such as cases, emails, or updates, Dynamics 365 CRM ensures the most actively used and relevant record is retained after merging duplicates.
Sometimes relevance is determined by activity, not fields.
Master selection can consider:
- Latest Case, Order, Invoice, or Email
- Record Created On / Modified On
Ensures the most actively used customer record survives.
Want to Configure Master Deciding Rules?
This overview explains the concept and business value of master deciding rules for merging duplicate records in CRM.
For exact configuration steps, role-based controls, and screenshots, refer to the detailed technical documentation.
Merge Rules & Conditions for Dynamics 365 CRM Record Merge
Merge rules and conditions define how Dynamics 365 CRM should handle duplicate records once they are identified.
They help decide whether duplicates should merge automatically, be reviewed by users, or be blocked entirely, ensuring every merge aligns with business intent and data governance policies. Should these records merge automatically, be reviewed, or be blocked?
Not all duplicates should merge.
What are the Merge Rule Actions for Record Merge in Dynamics 365 CRM
✅ Merge – Automatically merge duplicates
🔍 Review – Send duplicates for manual validation
⛔ Deny – Block merging entirely
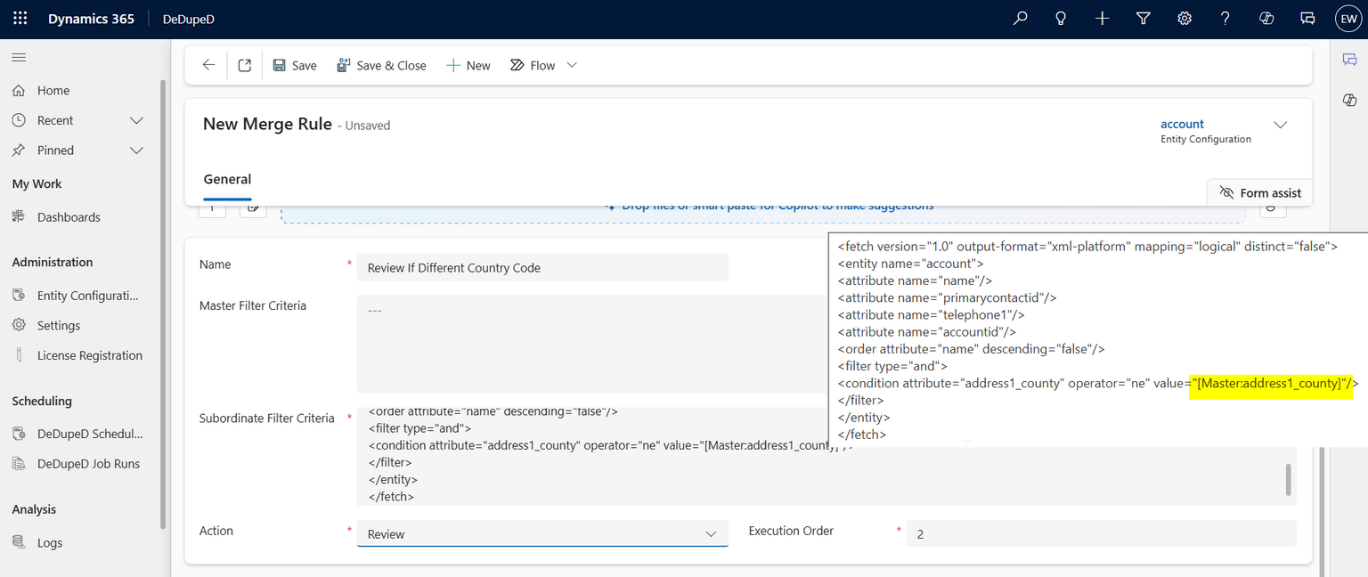
What are the Master & Subordinate Record Conditions in CRM?
Master and subordinate record conditions define how CRM decides which record should remain and how data from duplicate records should be handled during a merge.
These conditions evaluate both records side by side—comparing key attributes and values—to ensure the most accurate and relevant information is preserved after merging duplicates.
Merge Rules evaluate:
- Master record attributes (status, owner, source)
- Subordinate record attributes
- Field-to-field comparisons (e.g., Email = Master Email)
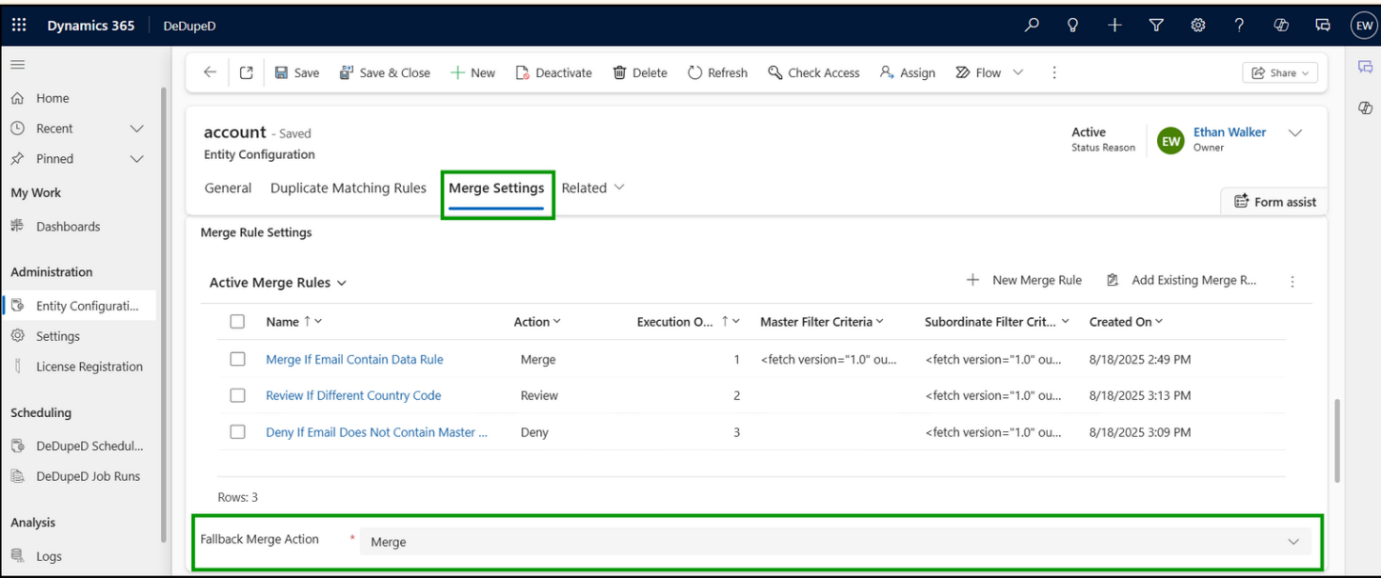
How does Execution Order & Fallback Behavior get executed while Merging Records in Dynamics 365 CRM?
Execution order and fallback behavior define how CRM consistently decides the outcome of a record merge. By evaluating rules in a predefined sequence and applying a clear fallback when no rule matches, Dynamics 365 CRM ensures merge decisions are predictable, controlled, and aligned with data governance standards.
- Rules execute in priority order
- The first matching rule determines the outcome
- If no rule matches, a fallback action (Merge / Review / Deny) is applied
Ensures deterministic, governed merge decisions.
Want to Configure Merge Rules?
This overview explains the concept and business value of merge rules for handling duplicate records in CRM.
For exact configuration steps, rule options, and screenshots, refer to the detailed technical documentation.
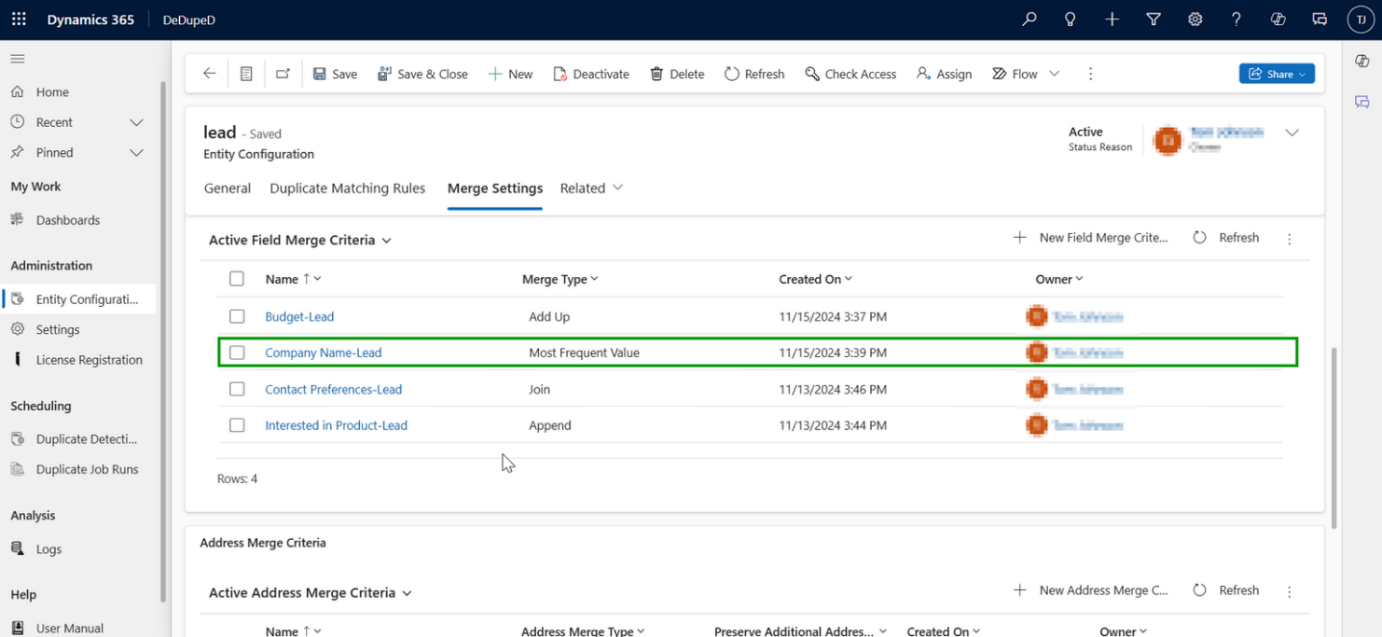
Field Merge Criteria for Merging Records in Dynamics 365 CRM
How to Decide Which Information is to Be Kept During Merges in Dynamics 365 CRM?
Field merge criteria define how individual pieces of information are combined when duplicate records are merged in Dynamics 365 CRM.
Instead of choosing data from just one record, CRM evaluates each field separately to ensure the most accurate, complete, and meaningful values are retained, based on how that information is used in real business scenarios.
How do field values merge in Dynamics 365 CRM to remove duplicates?
Different data types require different merge logic.
Supported Field Merge Types
- Append – Combine text values
- Join – Merge multi-select option sets
- Add Up – Sum numeric or money fields
- Most Frequent Value – Retain the dominant value
How to Retain Additional Values while Merging Records in CRM to Avoid Data Loss?
When field values conflict:
- The primary value remains on the master
- All other values are preserved in custom fields
Critical for audit, compliance, and AI enrichment.
Looking for the exact setup steps for field-level merge behavior?
Explore the technical documentation for detailed instructions and configuration options.
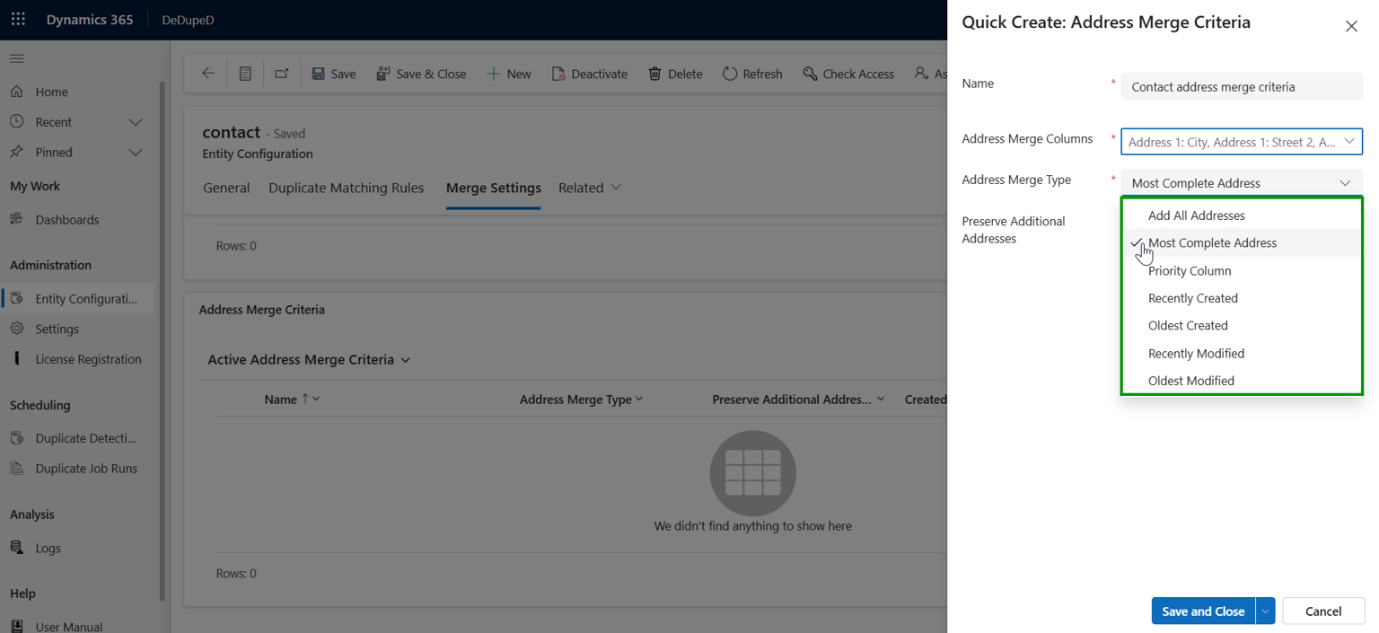
Address Merge Criteria for Merging Records in Dynamics 365 CRM
Address merge criteria define how address information from duplicate records is combined during a CRM merge, without overwriting or corrupting existing data.
By using structured merge logic instead of simple text replacement, Dynamics 365 CRM ensures that the most relevant, complete, and accurate address details are retained, while preserving important location data across Accounts, Contacts, and Leads.
How are addresses merged without data corruption in Dynamics 365 CRM?
Address data is structured, not simple text.
Supported Address Merge Strategies
- Add all addresses
- Most complete address
- Priority-based address
- Recently / Oldest Created
- Recently / Oldest Modified
Preserve Additional Addresses while Merging Records to Prevent Data Loss in Dynamics 365 CRM
When duplicate records are merged in Dynamics 365 CRM, valuable address information is often at risk of being lost.
Preserving additional addresses ensures that all relevant customer locations remain available after a merge, maintaining historical accuracy and supporting sales, service, logistics, and location-based decision-making.
When enabled:
- Non-selected addresses are retained
- Stored in the Customer Address entity
- Full address history is preserved
Essential for sales, service, logistics, and geo-analytics.
Need precise control over how address data is merged in CRM?
See the technical guide for setup steps, merge logic, and best practices.
Address Merge Limitation for Lead Entity
For the Lead entity:
- Preserve Additional Addresses is not supported
- Only the selected address is retained
This ensures predictable behavior during lead consolidation.
Relationship-Aware Duplicate Merging in Dynamics 365 CRM
What happens to activities and related records?
Duplicate merging is not limited to field values.
One-to-Many Relationships
- Activities (emails, calls, appointments)
- Notes and attachments
- Child records (cases, opportunities, orders)
All related records are rolled up to the master record.
Many-to-Many Relationships
- Marketing lists
- Associations with custom entities
Relationships are preserved and re-linked.
This ensures no loss of customer history.
Struggling with Duplicate Records in Dynamics 365?
Auto Merge & Governance
Auto Merge & Governance enables organizations to manage duplicate records automatically at scale, without relying on manual intervention.
It ensures duplicates created by background processes and system-driven operations are merged consistently, following defined governance rules to protect data accuracy and integrity across the CRM.
How duplicate merging runs at scale
Auto Merge enables server-side merging during:
- Data imports
- Power Automate flows
- Workflows
- Integrations
- APIs and assemblies
Prerequisite for Auto Merge
Auto Merge requires:
- At least one active, published duplicate detection rule
Without duplicate detection:
- Auto Merge will not trigger
Performance & Governance Controls
- Bypass plugins and workflows
- Prevent system bottlenecks
- Control execution during large operations
Merge Monitoring, Audit & Transparency
- Merged / Reviewed / Denied counts
- Execution status
- Record-level traceability
- Master record summary after merge
Required for compliance, audits, and AI trust.
Entity-Level Control Over Merge Logic
All merge configurations are applied per entity, including:
- Master Deciding Rules
- Merge Rules & Conditions
- Field Merge Criteria
- Address Merge Criteria
- Auto Merge enablement
This allows:
- Different logic for Accounts, Contacts, Leads
- Tailored behavior for custom entities
Manual Merge vs Auto Merge in Dynamics 365 CRM
Capability | Manual Merge | Auto Merge |
User-driven | ✅ | ❌ |
Bulk operations | ❌ | ✅ |
Integrations | ❌ | ✅ |
Governance & audit | ❌ | ✅ |
AI readiness | ❌ | ✅ |
FAQs
Which record should stay after merge?
The master record is selected using Master Deciding Rules based on activity, completeness, scoring, or business logic.
Does CRM automatically merge duplicates?
Yes. With Auto Merge enabled, duplicates can merge automatically during imports and integrations.
How do fields merge when duplicates are combined?
Fields merge using data-type-aware logic such as append, join, add up, or most frequent value.
Does CRM auto-merge addresses?
Yes. Address Merge Criteria define how addresses are selected or preserved.
What happens to other values?
They are retained using Retain Additional Values, ensuring zero data loss.
Reach out to us today to know more!