If you’ve been exploring Copilot and AI features in Microsoft Power Platform, you’ll notice a new column type in Dataverse: Prompt Column (Preview).
This feature allows you to save natural language prompts against a table, run them on your data, and store the AI-generated response in the same record. The generated text can then be used across apps, views, dashboards, and flows—just like any other field.
What is a Prompt Column in Dataverse?
A Prompt Column enables you to integrate generative AI into Dataverse tables. By defining a prompt and input fields, you can generate summaries, structured data, or documents automatically.
How Prompt Column in Dataverse work?
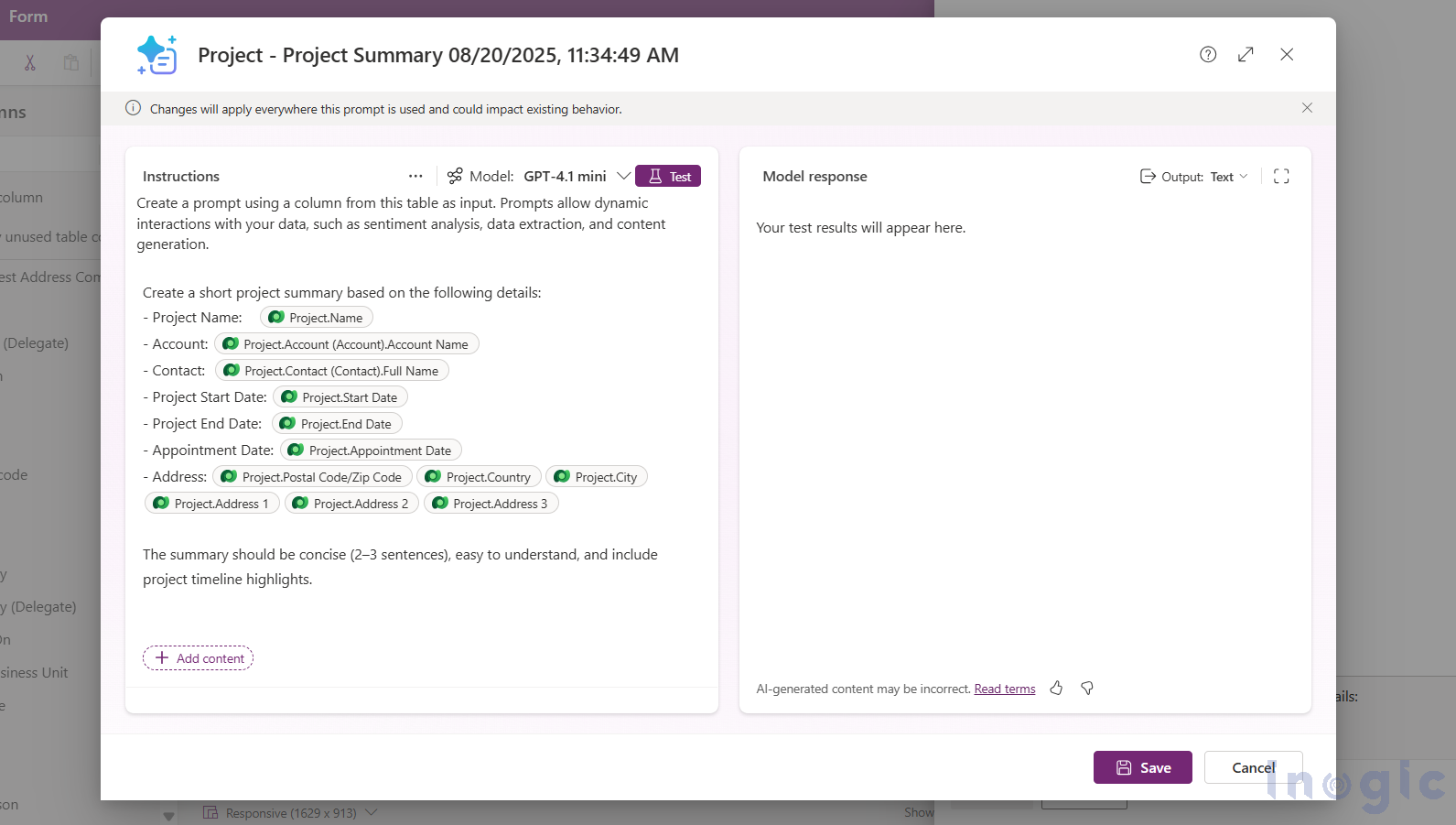
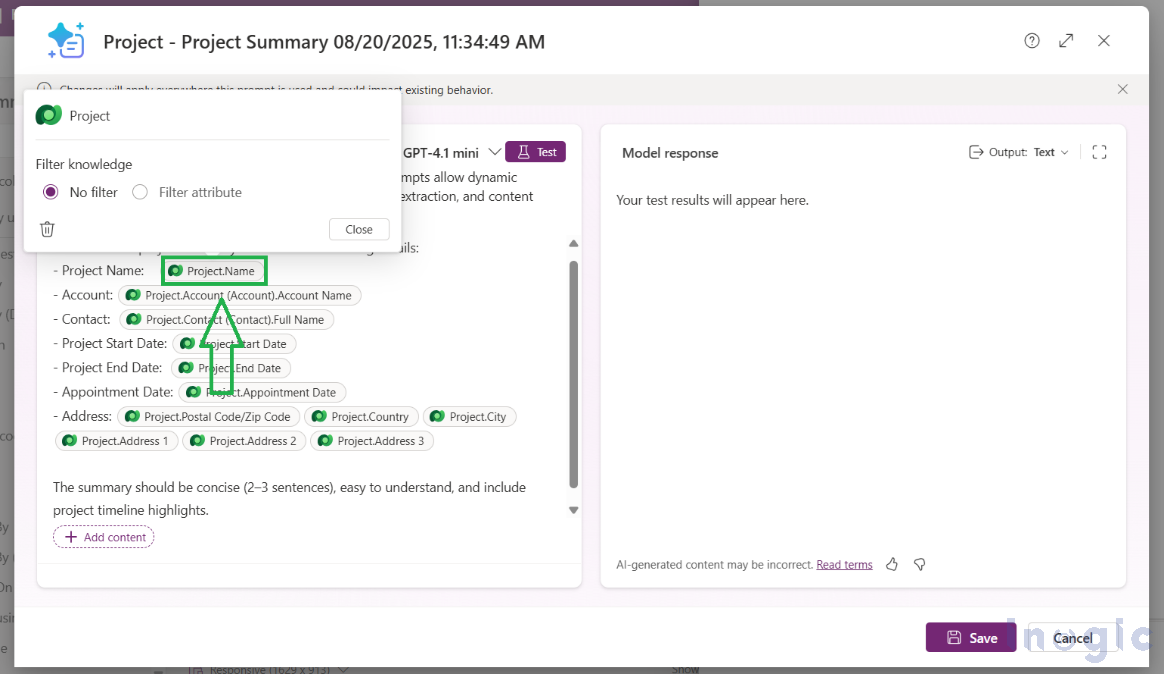
Say you store Project details in a table. You can add a Prompt column called Project Summary. The prompt could be like:
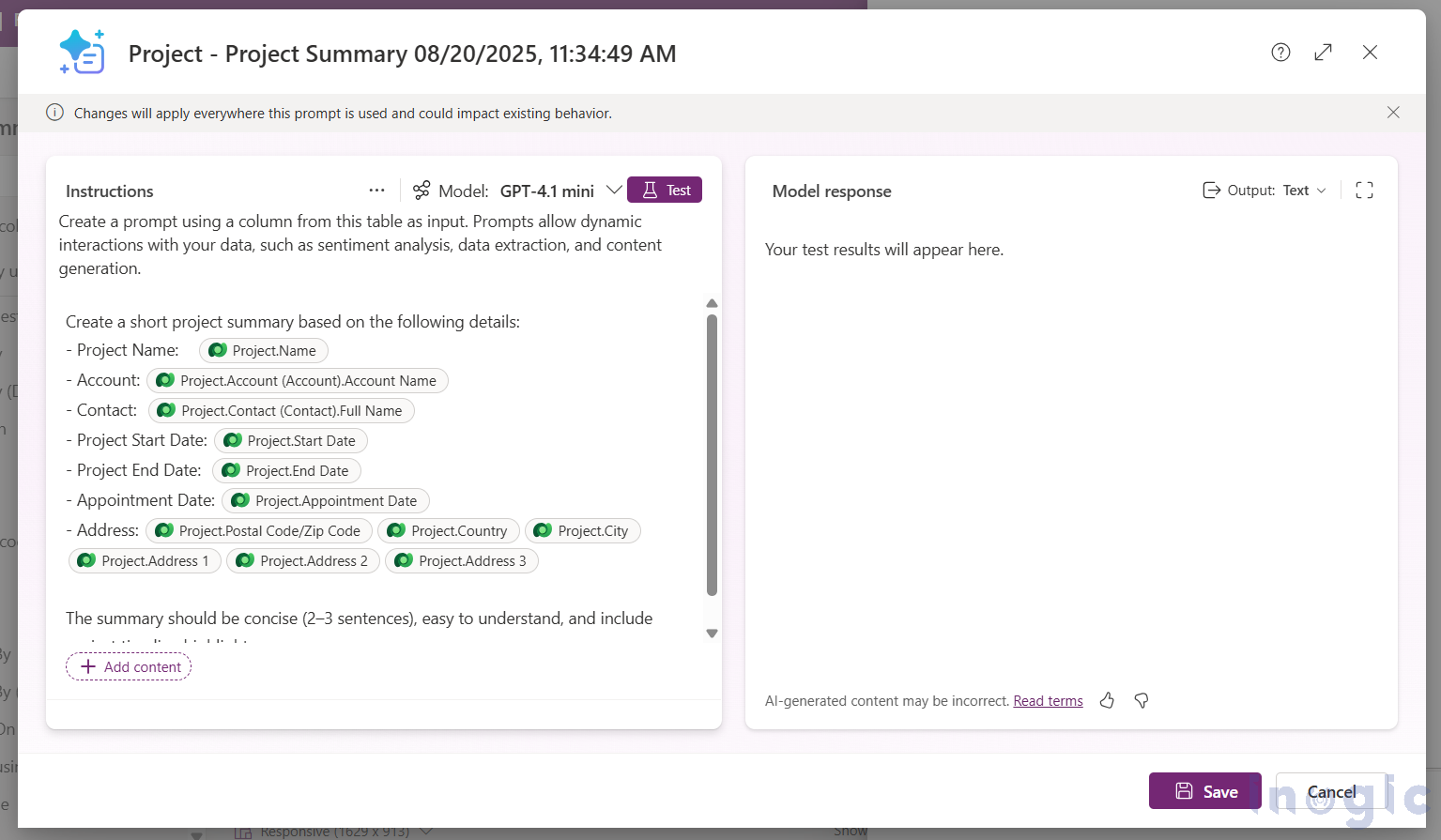
“Generate a concise summary of the project, including Project Name, Account, Contact, Start and End dates, Appointment Date, and Address. Keep it clear and professional in 3–4 sentences.”
When you set input columns such as Project Name, Account, Contact, Start Date, End Date, Appointment Date, and Address, the AI-generated summary is stored in the Project Summary column. This can be displayed in forms, added to dashboards, or used in workflows.
Prerequisites:
- Licensing: Prompt columns use the same model as AI Builder prompts (credits/messages depending on where you use them).
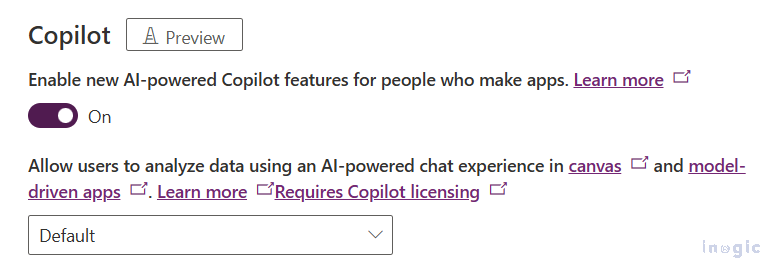
- Make sure Copilot and AI features are enabled in your environment settings before you start.
Navigate to Power Platform admin center → Environments → select your environment → Settings → Product → Features → enable Copilot and AI Builder prompts.
Create Your First Prompt Column (Step-by-Step)
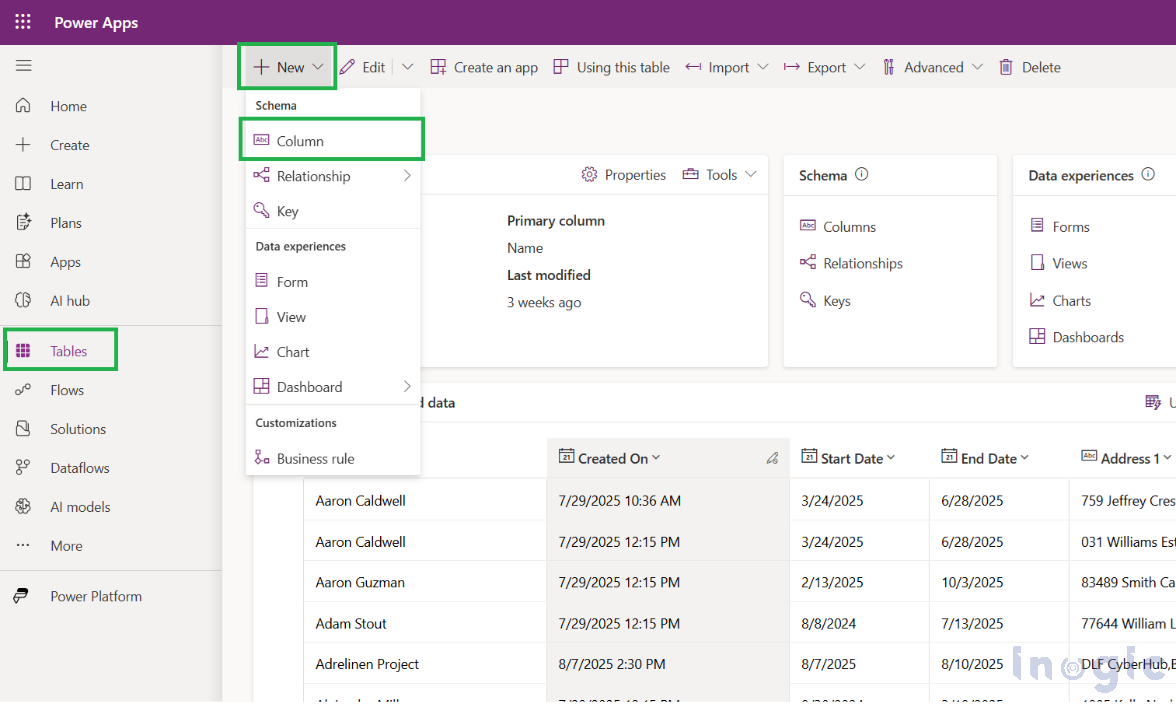
1. Go to Power Apps and open your table where you want to create the prompt column.
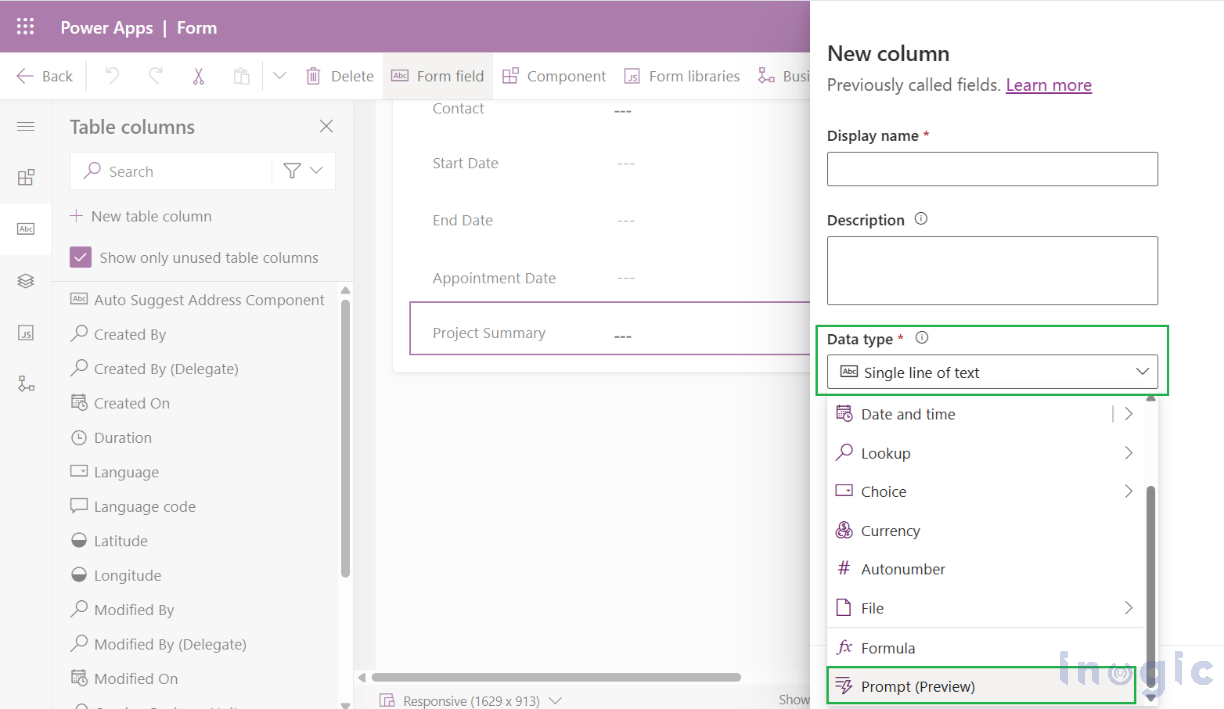
2. Click on New → Column → give it a name and description.
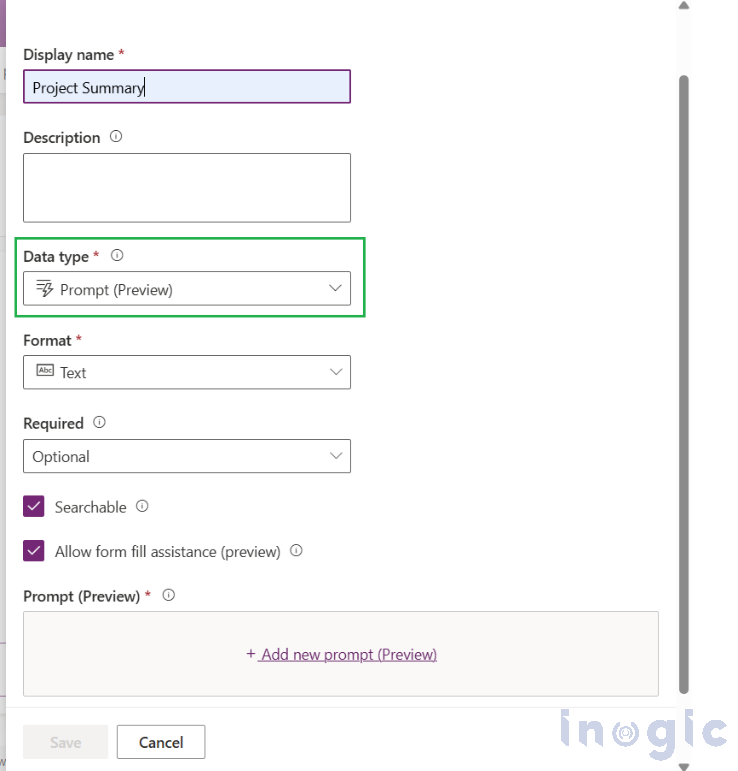
3. Set Data type = Prompt.
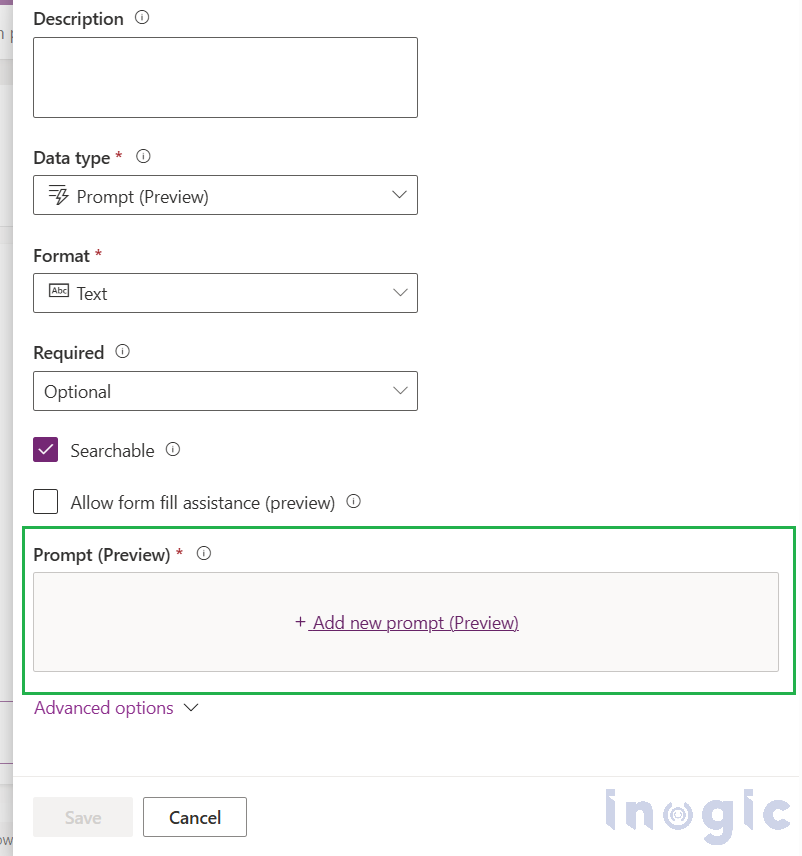
4. Clear “Allow form fill assistance.” (Recommended because this keeps the prompt focused) and then click + Add new prompt.
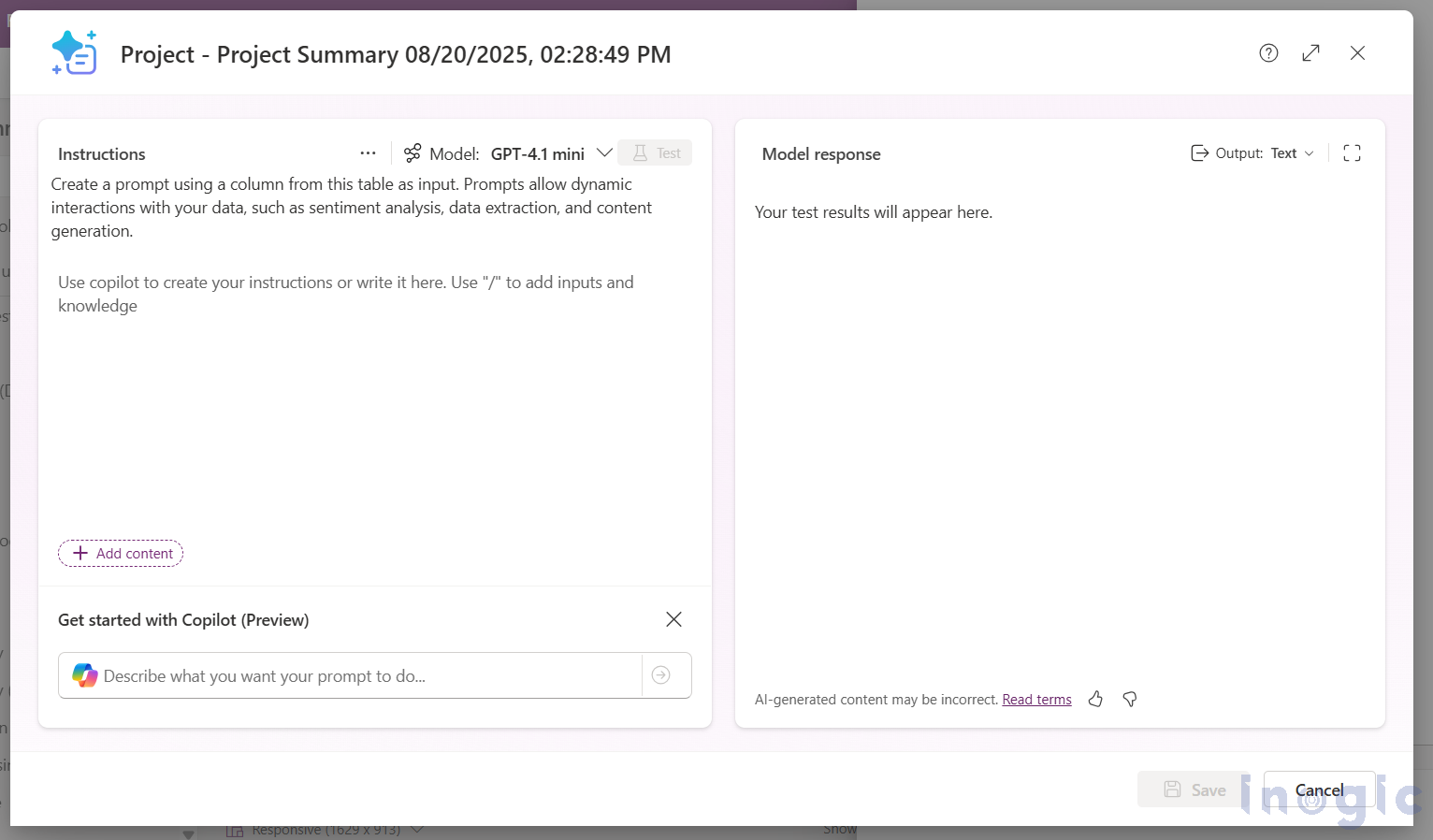
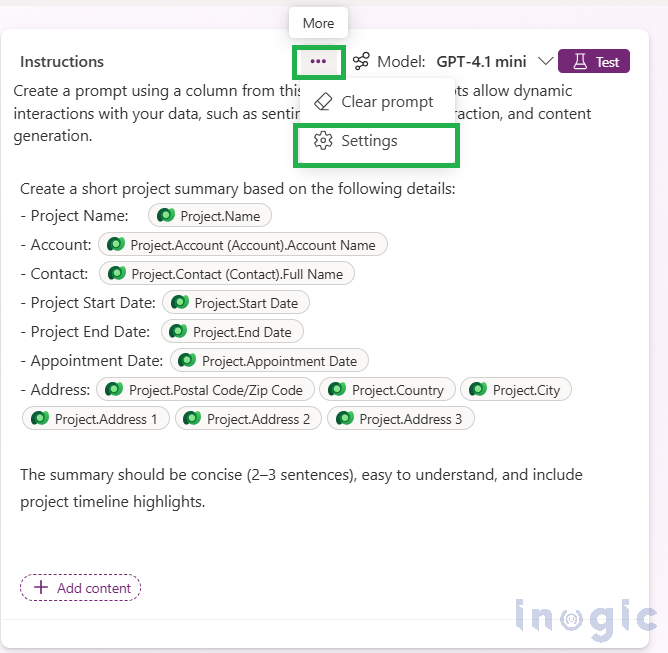
5. Write your custom prompt (or start from the template).
To remove the prefilled prompt, either delete the text manually or use the three-dot menu next to the Model field and choose the Clear prompt option.
6. Add input columns from your table (you can add multiple).
7. Save the prompt, and then Save the column.
Note:
- The limitations of the Prompts column are that you can create up to five prompt columns per table.
- Input columns can’t be formula columns, file, image, or another prompt column. If selected, they’ll be ignored.
- Prompt columns are currently created as Single line text fields. Multi-line text format isn’t supported yet. If your generated content is long, increase the column width on the form so the full output is easier to read.
Available AI Models
You can choose from:
- Basic GPT-4.1 mini (default)
- Standard GPT-4.1
- Premium o3
How to test the prompts in Dataverse?
1. Create a test record with realistic values in your input columns.
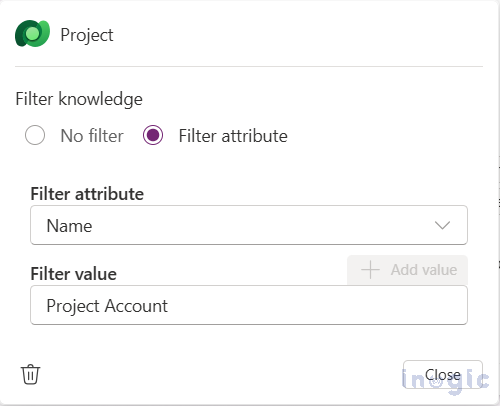
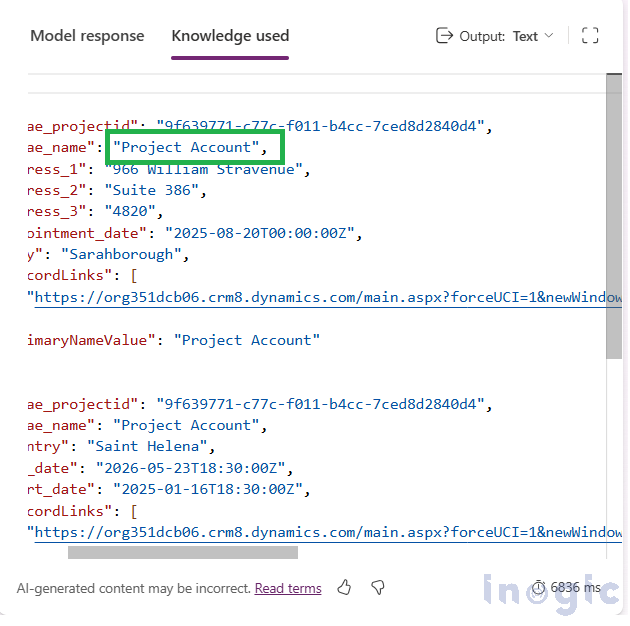
2. In the prompt editor, open Filter knowledge, pick a filter (e.g., Name), and target your test record so the model only uses that row’s inputs.
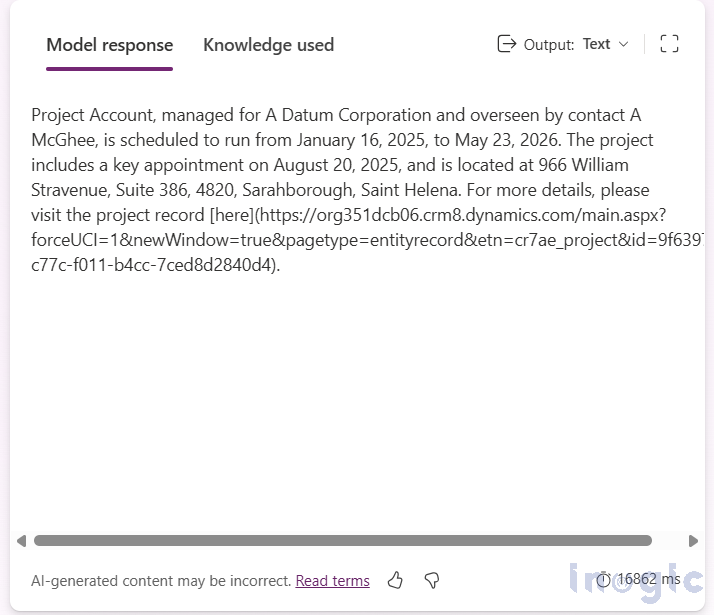
3. Click Test and review the Model response and Knowledge used tabs.
Model Response:
Model responses/output formats come in three types, selectable from the output option:
- Text – Returns a simple written response.
- JSON – Provides structured data that apps can parse.
- Document (Preview) – Generates a file output, like a summary or report.
Note: For this, you need to upload the document layout in a Word file format.
Knowledge Used:
4. Adjust wording until the output is consistent; Save.
Tip: Keep samples that “broke” your prompt—retest them after each change.
Making the AI output visible in your application
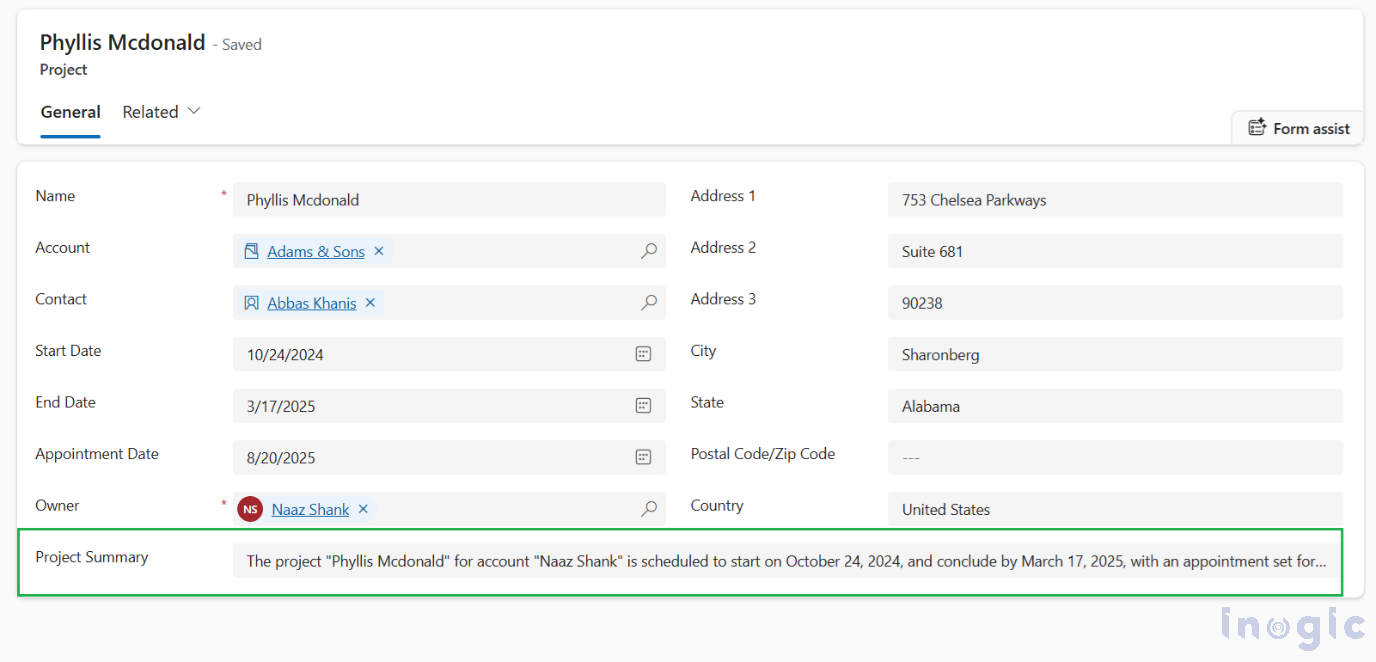
- Open or create a model-driven app, add your input, and prompt columns to the form, save and publish.
- Check the results on the form to validate the generated output for individual records
Note: For existing records, the prompt output won’t appear automatically. You’ll need to make a small update and save the record again to trigger the AI and generate the output.
Troubleshooting quick wins
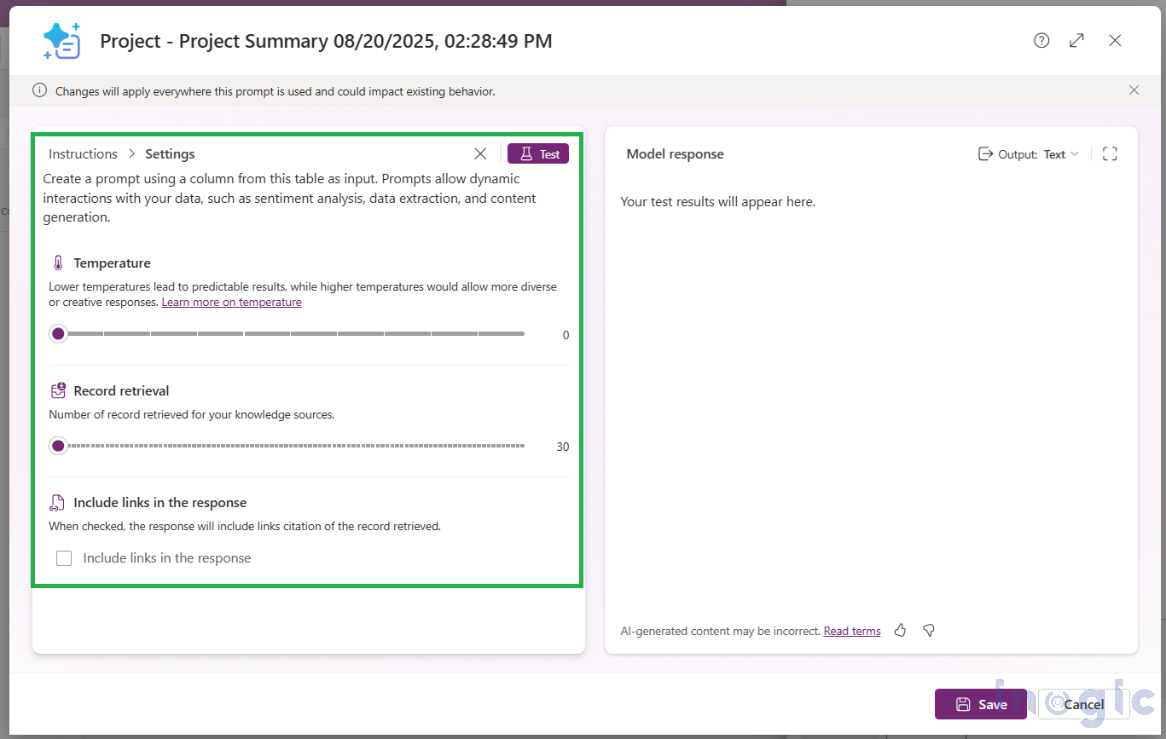
- Output is empty or low quality? → Adjust your prompt in Prompt Editor → Settings.
Now, clicking on the Settings option in the prompt editor lets you adjust how the AI generates responses by configuring temperature, record retrieval, and citation preferences.
- Temperature → controls how predictable or creative the response is.
- Record retrieval → sets how many records the model can pull as context.
- Include links in the response → adds citations to the output if checked.
- I don’t see the Prompt type → Check environment features and licensing; remember this is a preview and may be region/rollout dependent.
Note: Since this is a preview feature, you may occasionally encounter pop-up errors. These can happen due to complex prompts, unsupported input fields, or if your environment lacks sufficient AI Builder credits.
- Nothing happens on form → Ensure the Prompt column is on the form and the inputs have values; republish the app.
Key Benefits of Using Prompt Columns in Dataverse
- Automate content generation with AI.
- Ensure consistency across apps and workflows.
- Save time and improve user productivity in Dataverse and Power Platform.
FAQs
- What is a Prompt Column in Dataverse?
A Prompt Column is a special field that runs a generative AI prompt, takes inputs from other fields, and writes the generated text back into the record.
- How many Prompt Columns can I create in one table?
You can create up to five Prompt Columns per table.
- Which AI models are supported?
Basic GPT-4.1 mini, Standard GPT-4.1, and Premium o3.
- Can I use Prompt Columns in Model-Driven Apps?
Yes, you can display and use them like any other field in forms, views, and dashboards.
- Is this feature available globally?
Prompt Columns are in preview and may be region-specific.
Conclusion
A prompt column runs a generative AI prompt that you define, takes inputs from other columns in the row, and writes the generated text back to the column. You can then use that result anywhere Dataverse is used.
Prompt columns open up a practical way to use AI within Dataverse. Try creating one in your own tables, experiment with different prompts, and see how quickly it can turn raw data into meaningful insights.